INTERCARGO published its Bulk Carrier Casualty Report, reporting that 26 bulk carriers of over 10,000 dwt were declared as total losses for the years 2013-2022.
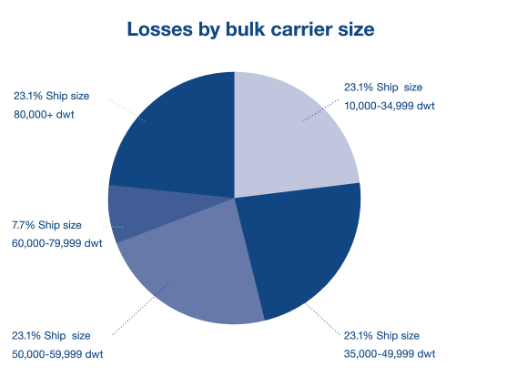
Ships lost by size
According to INTERCARGO, bulkers losses took place as follows:
- 80,000+ dwt: Six ships were lost, accounting for 23.1% of the total 26 casualties reported. There casualties cost 22 lives, or 21.2% of the total 104 lives lost during the period. In 2020 the losses of one Capesize and one VLOC vessel (Wakashio and Stellar Banner) focused attention on large bulk carrier safety.
- The lowest number of casualties occurred in the 60,000-79,999 dwt range, representing 7.7% of the total of 26 ship losses, with no fatalities.
- Other categories saw the loss of six ships with significant loss of life as a result. The 50,000-59,999 dwt range accounted for 55 seafarers’ lives, (52.9% of the total), 12 fatalities in the 10,000-34,999 dwt range and 15 in the 35,000-49,999 dwt range.
Causes of casualty
As for the causes of casualties, INTERCARGO reports that:
- Cargo liquefaction remains the greatest contributor to loss of life, accounting for 70 lives or 67.3% of the total loss of life in the past ten years.
- Grounding remain the greatest cause of ship losses, with 12 losses or 46.2% of the total.
- Three casualties (11.5% of the total) were a result of flooding and these cost 22 lives – a significant 21.2% of the total number of lives lost.
- The average life loss per ship casualty was 4.00 during the ten-year period between 2013 and 2022 and 3.41 between 2012 and 2021. This compares to 3.56 during 2011 and 2020.

Flag state performance
At the end of January 2023, 19 of the 26 bulk carrier losses in this analysis had investigation reports made available on IMO’s GRISIS (Global Integrated Shipping Information System) database. That represents 73.1% of the total.
The average time from an incident to a report becoming available on GISIS has been 28.2 months for these investigations, with the shortest 7 months and the longest 52.5 months.
The following analysis shows those casualties that have been reported by flag states and appear on the IMO GISIS database.