The UK Royal Society issued a report presenting the opportunities and challenges associated with the manufacture and future use of zero-carbon ammonia, in line with the global goals towards a sustainable and greener future.
The production of ammonia plays a major role in shipping’s decarbonization and has the capability to impact the transition towards decarbonization, despite its current use in fertilizer production.
The report indicates that green ammonia could also be used as:
- As a medium to store and transport chemical energy, with the energy being released either by directly reacting with air or by the full or partial decomposition of ammonia to release hydrogen.
- As a transport fuel, by direct combustion in an engine or through chemical reaction with oxygen in the air in a fuel cell to produce electricity to power a motor.
- To store thermal energy through the absorption of water and through phase changes between material states (for example liquid to gas).
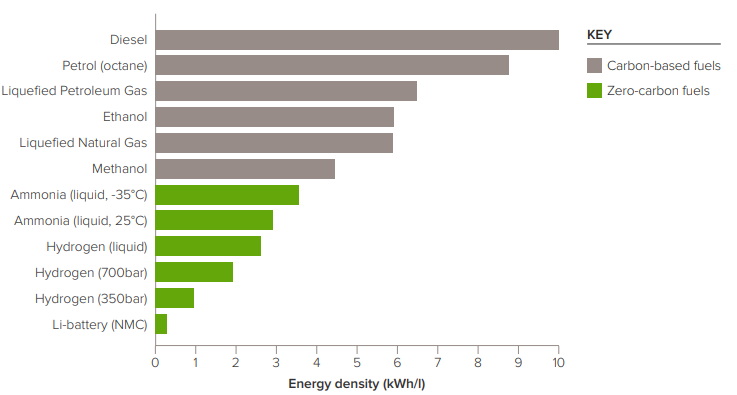
Given that ammonia has a relatively high energy density of around 3 kWh/litre and existing global transportation and storage infrastructure, it could form the basis of a new, integrated worldwide renewable energy storage and distribution solution.
These features suggest ammonia could readily be a competitive option for transporting zero-carbon energy by road, rail, ship or pipeline.
It is also stated that ammonia production accounts for about 1.8% of global carbon dioxide emissions.
Yet, for the time being the use of ammonia comes with several challenges.
Human alteration of the global nitrogen cycle, mainly through the application of ammonia based fertilisers, is a contributor to global declines in biodiversity, widespread air quality problems and greenhouse gas emissions across the world.
Therefore, new uses of ammonia in the storage, transportation and utilization of renewable energy, must therefore be decoupled from environmental impact, with emphasis on avoiding and effectively eliminating emissions of nitrogen oxides and ammonia release.
To find affordable and effective solutions to the challenges explained above, technical feasibility is needed, as well as the development of the appropriate regulations and implementation of safety procedures, to achieve more flexible routes on a global scale towards a low-carbon energy future.
Over the coming decades, ammonia has the potential to make a significant impact through enabling the transition away from our global dependence on fossil fuels and contributing, in substantial part, to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
To learn more click herebelow

See also: