The Black Sea MoU has published its Annual Report for 2024, detailing its actions and presenting key Port State Control (PSC) data.
As informed, the 2024 reporting period was significantly impacted by the ongoing armed conflict between the Russian Federation and Ukraine, which continued to pose serious risks to the safety and security of crews and vessels operating in the region, conflicting with the BS MoU’s objectives.
Overview of inspections conducted in 2024
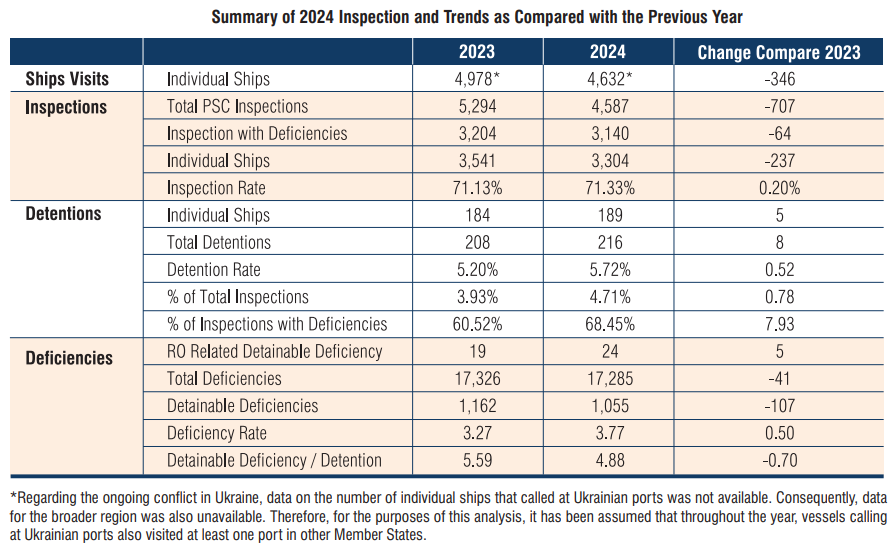
Throughout 2024, a total of 4,587 inspections were conducted on 3,304 individual ships in the Black Sea Region, covering ships registered under 70 Flag Administrations. This represents a 13.4% decrease compared to the 5,294 inspections conducted in 2023. Notably, this marks the second-lowest number of inspections since the establishment of the Black Sea MoU on PSC, with the only lower figure being 4,499 inspections in 2007. Furthermore, the number of individual ships inspected in 2024 was the lowest recorded to date.
Rise in average detention rate
A key observation in 2024 was the significant increase in the average detention rate, which rose to 4.71%, reflecting a notable upward trend since 2021. This increase underscores the growing necessity for robust Port State Control mechanisms to ensure maritime safety and regulatory compliance in the region.
Data limitations and inspection rate assumptions
Due to the ongoing war in Ukraine, exact data on the number of individual ships operating in the region was unavailable. As a result, data for the broader region was not accessible. Therefore, for the purposes of this analysis, it has been assumed that vessels calling at Ukrainian ports also visited at least one port in other Member States. Based on this assumption, the regional inspection rate for 2024 was determined to be 71.33%.
Increase in inspections with deficiencies
Out of 4,587 inspections conducted in 2024, 3,140 were found with deficiencies. This percentage continued its upward trend and peaked at 68.45% of all inspections.
Detentions and flag administration distribution
A total of 216 vessels were detained in 2024 due to deficiencies clearly hazardous to safety, health, or the environment. These vessels were registered under 32 different Flag Administrations. The overall detention percentage in the region (detentions as a percent of inspections) increased from 3.93% in 2023 to 4.71% in 2024, continuing its upward trend. Additionally, as several individual ships were inspected and detained more than once during the year, the regional detention rate in 2024 (individual ships detained as a percent of individual ships inspected) also showed an upward trend, reaching 5.72%.
Ship type breakdown of inspections
When considering the breakdown of ships inspected by ship type, the largest group of the ship inspected during 2024 were general cargo/multipurpose ship, which accounted for 1,747 inspections (38.09%). This was followed by bulk carriers with 1,516 inspections (33.05%) and oil tanker/chemical tanker with 500 inspections (10.90%). Together, these three ship types represented 82.04% of all inspections.
Age distribution of inspected ships
In 2024, the largest proportion of inspected ships were the 16–20 year age range, accounting for 1,304 inspections (28.43% of total inspection) and followed by ships more than 35 years old with 771 inspections (16.81%) and ships 11–15 years old with 627 inspections (13.67%).
Most frequent deficiencies recorded
In 2024, a total of 17,285 deficiencies were recorded during the port State control inspections. The most frequently identified deficiencies were related to safety of navigation with 2,562 deficiencies (share of total deficiencies: 14.8%), life-saving appliances with 1,804 deficiencies (10.4%), health protection, medical care, social security with 1,750 deficiencies (10.1%), fire safety with 1,655 deficiencies (9.6%) and documents with 1,286 deficiencies (7.4%). These five categories collectively accounted for 52.3% of all deficiencies recorded in 2024.

ISM-related deficiencies
In 2024, a total of 386 deficiencies were related to the International Safety Management (ISM), representing 2.23% of all recorded deficiencies. Of these, 76 were marked as detainable deficiencies, accounting for 7.20% of all detainable deficiencies.
Most common detainable deficiencies
A total of 1,055 detainable deficiencies were recorded during PSC inspections in 2024. The most common detainable deficiencies were related to safety of navigation with 168 deficiencies (share of total detainable deficiencies: 15.9%), fire safety with 133 deficiencies (12.6%), emergency systems with 117 deficiencies (11.1%), life-saving appliances with 82 deficiencies (7.8%) and ISM with 76 deficiencies (7.2%). These five categories represented 55.6% of all detainable deficiencies recorded in 2024.