The Maritime and Port Authority (MPA) of Singapore, has released a media statement on its efforts and plan on achieving better efficiency, safety, and productivity through technology.
Tuas Port, which opened in September of 2022, when completed in the 2040s, it will be the world’s largest fully-automated terminal, with a handling capacity of 65 million twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs), almost double the handling volume of 37.3 million TEUs handled in 2022.
To further maritime digitalisation and the development of future concept of operations, MPA and Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) in August 2022 to provide full maritime 5G coverage in our major anchorages, fairways, terminals and boarding grounds by mid-2025.
Twelve maritime 5G base stations will be set up to complement the onshore 5G communication infrastructure. Three of the base stations will be ready by 2023 to support testing and development of new digital applications, such as remotely assisted pilotage advisory, digital bunkering, delivery drones, and telemedicine. The remaining nine base stations will be set up by 2025.
To further strengthen vessel navigational safety and efficiency of the port as we continue to grow our hub port, MPA is developing an artificial intelligence-enabled Next Generation Vessel Traffic Management System (NGVTMS) to replace the existing Vessel Traffic Information System (VTIS).
…MPA Singapore stated.
With data analytics and machine learning to identify traffic hotspots as well as advanced algorithms to predict potential collisions, the NGVTMS will allow MPA to provide Ship Captains with more accurate and timely information to take early actions for navigational safety. Secured and reliable data transfer between ship-ship and ship-shore for NGVTMS can be facilitated through various connectivity platforms such as the VHF Data Exchange System (VDES) and the maritime 5G network.
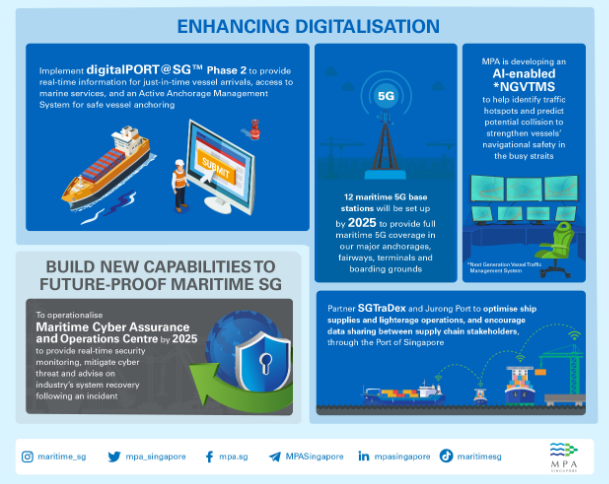
Furthermore, MPA will work with Singapore Trade Data Exchange (SGTraDex), Jurong Port and their partners to pilot a data sharing initiative under SGTraDex’s ship supplies and lighterage optimisation use case that focuses on supplies procurement, fulfilment and lighterage logistics. The pilot aims to help large and small businesses optimise their ship supplies operations by digitalising their ship supplies operations, and encouraging data sharing between supply chain stakeholders in the ship supplies sector.
With regards to cyber security, MPA will establish the Maritime Cyber Assurance and Operations Centre (MCAOC) by 2025 to provide real-time security monitoring and disseminate information to mitigate cyber threats, advise on system recovery and measures to take following an incident, and facilitate cyber threat information-sharing among maritime stakeholders such as port and terminal operators, shipping lines and marine service providers with digital systems.
Equipped with analytics capability, MCAOC will strengthen operational responses to evolving cyber threats by providing insights to maritime stakeholders on advanced malware and modes of attack. MCAOC will also offer training and conduct cybersecurity exercises for the maritime industry.
Reducing carbon emissions in Maritime Singapore

MPA will set the target for the harbour craft and pleasure craft sectors to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050 in support of Singapore’s 2050 national net-zero target. To achieve this transition, from 2030, all new harbour craft operating in our port waters must be fully electric, be capable of using B100 biofuel, or be compatible with net-zero fuels such as hydrogen.
To help the industry meet the 2030 requirement, MPA encourages the industry to consult with MPA on the owners’ electric, B100 or hydrogen compatible harbour craft designs early. The consultation process will be a compulsory requirement from 2027.
MPA will support the development of electrification technology through the following initiatives:
- Research, design, build and operate full-electric vessels
- Conduct trials of full-electric vessels
- Work with research institutes to study the charging infrastructure required to support an electric harbour craft fleet
- Partner with industry, financial institutions, harbour craft operators and manufacturers to lower costs of adoption and mobilise support for early adopters.
- Collaborate with industry to enhance energy efficiency and reduce emissions of existing harbour crafts in the near term
Pathways for Alternative Fuels
To prepare Singapore for a multi-fuel bunkering future, MPA has developed the world’s first marine biofuel provisional standard in consultation with the industry and researchers for biofuel blends of up to 50% or B50. This standard will be updated progressively as trials for biofuel blends of up to 100%, or B100 are carried out, and is expected to be completed by 2025. Singapore’s Maritime Energy and Sustainable Development Centre of Excellence will also be releasing the findings of its compatibility study on various biofuel types and percentage blends for our harbour crafts by end March 2023.
Aside from biofuels, MPA is exploring the use of hydrogen and ammonia to support the decarbonisation of international shipping. In December 2022, MPA and the Energy Market Authority launched an Expression of Interest (EOI) to build, own and operate low or zero-carbon ammonia power generation and bunkering solutions on Jurong Island. The EOI is open until end April 2023.
Green and Digital Shipping Corridors
In August 2022, MPA signed a MOU with the Port of Rotterdam to establish the world’s longest “Green and Digital Shipping Corridor (GDSC)”. The corridor will pilot the deployment of digital solutions, support investment in green infrastructure, and develop enablers to accelerate low and zero carbon shipping.
Singapore is actively engaging other like-minded ports and country partners to establish more corridors. Recently, MPA, Port of Los Angeles, Port of Long Beach and C40 Cities started discussions to establish a GDSC between Singapore and the San Pedro Bay port complex.


































































