In its latest safety awareness bulletin, the Australian Maritime Safety Authority (AMSA) highlights the crucial role of maintenance in ensuring safe operations onboard.
According to AMSA, maintenance ensures that a system continues to perform its intended function as per its design in relation to the level of safety and reliability. In 2023, there were 3555 technical incidents reported to AMSA, compared to 3672 in 2022. Analysis of AMSA’s port State and flag State control inspection data shows there were 525 maintenance-related deficiencies issued in 2023 and 415 in 2022. There has been a gradual increase in maintenance-related deficiencies issued since 2019.
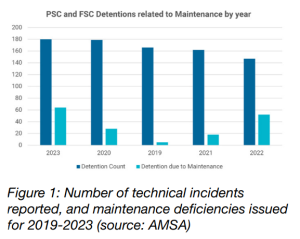
In 2023, there were 180 port State and flag State detentions and 147 detentions in 2022. Of these, 64 or 35.6 per cent were due to maintenance issues in 2023 and 52 or 35.4 per cent in 2022. Technical failures are often considered isolated incidents, and therefore most of these do not undergo further investigation.
Examples of issues that could lead to technical failures include but are not limited to:
- Unsuitable modification to parts
- Omission of maintenance checks
- Incomplete installations
- A fault not being isolated
- Missing equipment.
While many maintenance-related errors may seem inconsequential, they have the potential to remain dormant and can affect the safe operation of a vessel over time. Effective and regular maintenance will result in fewer machinery failures and breakdowns. This in turn will minimise the rate of unforeseen operational delays and serious incidents. There are also the added cost-related benefits of improved productivity and efficiency.
Regulatory compliance: ISM Code
A planned maintenance system to maintain a vessel and its equipment is a requirement of the ISM Code (Clause 10). The ISM Code outlines that the company/operator should inspect equipment and technical systems at appropriate intervals as part of a vessel’s safety management system and manufacturer requirements. This includes ensuring non-conformities are reported and appropriate corrective actions are taken, as well as regular testing of equipment or technical systems that are not in continuous use.
































































