ITOPF has published a report explaining the potential damage & liabilities arising from a shipping incident involving a li-ion battery powered vessel.
As explained in the “Fate, Behaviour, Potential Damage & Liabilities Arising from a Shipping Incident Involving a Li-ion Battery Powered Vessel” report, at least half of existing vessels with li-ion batteries utilise the technology as part of a hybrid system paired with a traditional combustion engine using conventional fuels (or possibly biofuels).
Li-ion batteries can be considered as inert when functioning normally and do not pose the same risk of pollution as the fuel oils in traditional combustion engine propelled vessels. However, if damaged, Li-ion batteries have the potential to undergo thermal runaway, generate large vapor clouds, and result in vapor cloud explosions.
The point at which a battery will go into thermal runaway cannot be predicted with certainty but is more likely to occur after excessive heat exposure, if the battery is physically damaged, or is overcharged. Increased heat production increases the reaction rate, in turn producing more heat, which then leads to uncontrolled positive feedback: the thermal runaway.
The sharp rise in internal battery temperature causes the inner structures of the battery to destabilize and degrade, which leads to failure of the battery. This will result in extremely high temperatures and may lead to jet-like flames emanating from the battery on very short timescales (seconds to minutes).
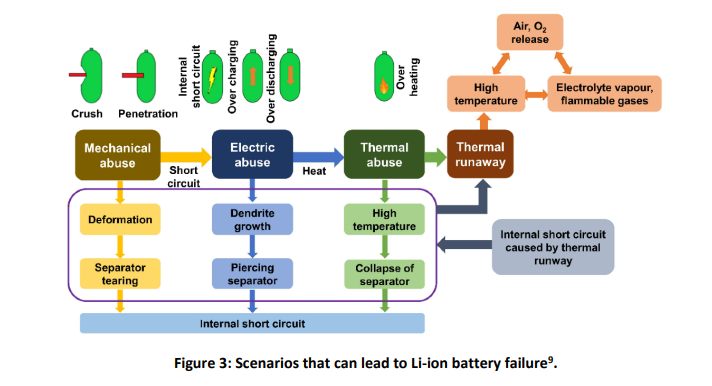
This is a self-sustaining heat source that is challenging to extinguish, with the potential to reignite hours to days after the initial flames have been extinguished. If a battery undergoes thermal runaway, the resulting flames and/or explosion are likely to result in the propagation of thermal runaway to neighboring battery units.
When a Li-ion battery enters thermal runaway, prior to ignition, a large white vapor cloud will be produced. The greater the power density of the battery, the greater the amount of gas likely to be produced.
Li-ion battery fires & maritime incidents
Li-ion batteries within a propulsion mechanism are not necessarily more prone to fire compared to traditional combustion engines, however, the consequences can be more significant because they are far more difficult to extinguish and are capable of spontaneously reigniting hours or days after the initial fire has been extinguished. From recent industry experience of incidents involving Li-ion battery-powered electric vehicles (EVs) being transported at sea, the speed at which thermal runaway initiates and the ability of the Li-ion batteries to sustain fire may lead to the vessel sinking or being declared a constructive total loss (CTL).
Hazards of Li-ion battery incidents
Flammability
A Li-ion battery in thermal runaway provides a self-sustaining ignition source. The vapor cloud produced during thermal runaway is made up of a number of flammable gases, therefore a sustained fire is likely. If gases are vented at high pressure, jet-like flames may be produced. Given that thermal runaway produces a self-sustaining heat source and generation of oxygen, Li-ion fires can be difficult to extinguish. Extinguishing external flames will not remove the risk of fire; the internal battery temperature must be reduced, and thermal runaway stopped to prevent further fire. Batteries undergoing thermal runaway are also prone to reignition hours to days after the initial flames are extinguished.
Explosion
If the Li-ion battery undergoes thermal runaway but the gases do not escape the battery unit, a confined VCE is likely to happen with little warning. The explosion is likely to cause ejection of shrapnel. If the gases vent from the battery into the surrounding area during thermal runaway, there may be a delayed explosion or ignition if the gas saturates a confined area.
If a Li-ion battery has entered into thermal runaway and is emitting flames, any response measures that extinguish the fire without reducing the battery temperature and halting internal thermal runaway may change the primary hazard from fire to explosion.
Toxicity
Several gases emitted during thermal runaway are considered toxic, but the exact composition of the vapor cloud depends on the type of battery being used. The gases of most concern in terms of toxicity are carbon monoxide (CO), benzene (C6H6), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), hydrogen chloride (HCl), hydrogen fluoride (HF), hydrogen cyanide (HCN), and toluene (C7H8). When considering the relative quantity of gas produced and the Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health (IDLH) values, laboratory studies have shown that CO, NO2, and HCl will be the first gases to reach their IDLH values. The IDLH values of many of the toxic gases are lower than the approximate LEL. Therefore, the atmosphere is likely to be toxic to levels damaging to human health before it reaches its ignition level.
Corrosivity
Several of the gases likely to be produced when a battery enters into thermal runaway are corrosive. Of particular note are HCl, HF, and HCN. Following exposure to the water vapor naturally present in air, these corrosive gases will form dense white corrosive vapors.
Asphyxiant
Like with any gas in a confined environment, such as a vessel engine room or cargo deck, high concentrations of vapors can displace oxygen in the air, decreasing oxygen availability and therefore leading to asphyxiation to those present in these confined environments without suitable breathing apparatus.
Ecotoxicity of firefighting water run-off
Large quantities of water are typically used to manage Li-ion batteries in thermal runaway. However, since Li-ion batteries contain various metals and solvents, and the vapor cloud also contains several harmful gases and heavy metals, the impact of the firefighting water run-off should be considered.
In addition, there is evidence that thermal runaway in Li-ion batteries can continue even when submerged in water. There is little research into the impacts of such an incident, but any gases that are released into the water may dissolve or rise to the surface, and there may be impacts to the environment linked to any dissolved toxic gases.
Key points for consideration
#1 Legal framework
Pollution relating to vessels powered solely by Li-ion batteries is not covered specifically by an International Convention at present, with liabilities relating to a Li-ion battery incident a matter of national legislation. Li-ion batteries transported as cargo are classed as dangerous goods by the IMDG code.
If batteries are used as part of a hybrid propulsion system, damage and liabilities arising from the hybrid fuel (oil, biofuel, ammonia, methanol, etc.) should also be considered. In addition, a spill of cargo from a vessel powered in whole or in part by Li-ion batteries may result in additional damage and/or liabilities not considered here.
#2 Clean-up and Preventive Measures
In comparison to the costs associated with clean-up and preventive measures from a traditional spill of persistent hydrocarbon bunker fuel oil, the costs for this claim heading for a Li-ion battery incident would likely be for different measures, primarily limiting/managing thermal runaway, firefighting, and monitoring.
The rehabilitation of wildlife is another potential cost associated with clean-up and preventive measures.
#3 Personal Injury and Loss of Life
This claim heading is included within the HNS Convention for Li-ion batteries cargoes. Although incidents involving Li-ion battery propelled vessels are not covered by the HNS Convention, this claim heading is equally relevant to such incidents.
#4 Environmental Damage
The environmental impact of Li-ion battery incidents in the marine environment is not as widely researched as the impact associated with spills of other, more persistent, hydrocarbon oils. However, due to the fate, behavior, and chemical hazards of a Li-ion battery in thermal runaway, only a short-term, acute negative impact in the immediate vicinity of the incident location is expected.
#5 Property Damage
Costs arising for property damage will be spatially confined to properties in close proximity to the incident.
#6 Economic Loss
Economic loss can be split into “consequential loss,” whereby compensation is payable for loss of earnings suffered by the owners of property that have been impacted, and “pure economic loss,” whereby compensation is payable for loss of earnings suffered by persons whose property has not been impacted. In the event of a Li-ion battery incident, both consequential and pure economic loss could be experienced.
In conclusion, given the risks associated with batteries in thermal runaway, claims arising from such incidents would greatly contrast those associated with conventional persistent hydrocarbon oil spills.






























































