IMCA issued a safety flash that focused on a pollution accident that occurred during bunkering operations. Specifically, the incident took place as the vessel took bunkers supplied by five tanker trucks, one after the other. Because of difficulties during the bunkering operations, the hose was loosened resulting to the oil spill. As a result, the local Coast Guard was informed and arrived at the area of the incident.
The Incident
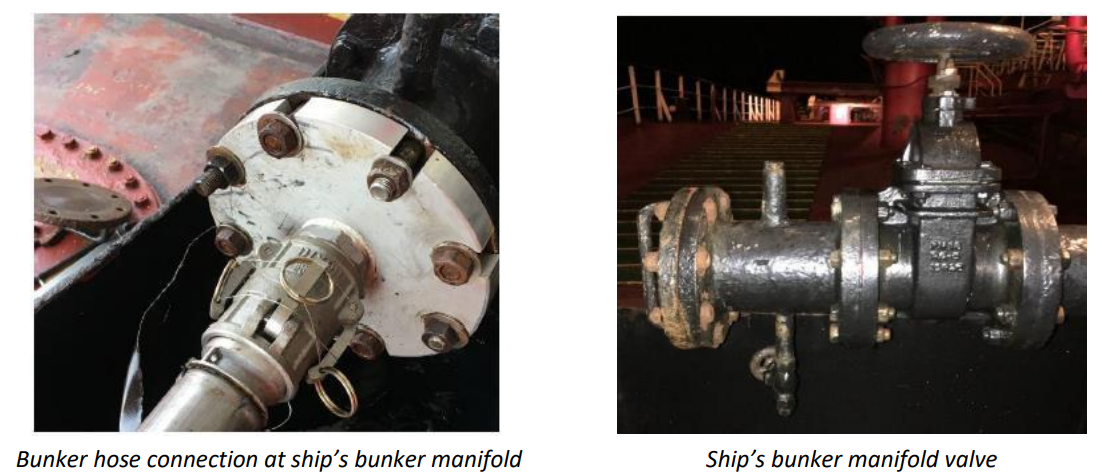
During the bunkering operations of a vessel, there was a spillage of approximately three litres of fuel. The pollution was due to the hose coupling that was loosened during fault-finding.
Mainly, the bunker hose was connected to the manifold of the first truck.
When the bunkering operation had already started for four minutes, the truck driver complained of back pressure, resulting the operations to be halted.
After the driver’s complaints, the Chief Engineer came to investigate the situation to find out the reason of back pressure. As he suspected that the manifold valve was not properly operating, he instructed the Fitter to open the hose.
As a result, after the hose was loosed, fuel oil sprayed out onto the pier due to pressure in the pipe.
Disconnection was stopped immediately, and the spilt oil was contained in the save-all at the manifold.
The Coast Guard that arrived to investigate, instructed the crew to clean up the oil on the pier and retain the sweepings onboard.
Clean-up on deck and pier was done using the vessel’s SOPEP equipment. Reports were made to all concerned parties as required. No restrictions were placed on the vessel by the Coast Guard or the port.
Probable Causes
According to IMCA the immediate cause was carelessness. The Chief Engineer didn’t think much of the problem and decided to open the hose coupling without checking if the bunker line was drained properly.
Additional casual factors were inadequate planning and inadequate maintenance/supervision.
Yet, the root causes were:
- The Chief Engineer was not able to methodically diagnose the reason for the back pressure and did not consider the risks involved in opening the hose coupling without checking that the line was not pressurized;
- There was no check of residual oil in the line by opening the drain dock;
- No instruction was given to the truck driver to open the truck valve to allow the oil to drain back into the truck.
Actions Taken
After the pollution incident, a full detailed review of bunkering procedures occurred.

































































una de las causas que, propician un derrame de combustible al inicio de una faena de combustible es el flange no correcto , ya que algunos barcos tienen flanges en en pulgadas, otros metricos, diferentes normas.-
Ahora la pregunta, existe alguna norma que indique el tipo de flange a conectar en lel buque, segun su tonelague u otra referencia, o clasificacion.-