McKinsey has published its tenth Women in the Workplace 2024 report, collecting information from 281 participating organizations that collectively employ more than ten million people.
The report reveals that while women’s representation in corporate roles has increased modestly over the past decade, significant disparities persist at various management levels. Women now hold 29% of C-suite positions, a notable increase from 17% in 2015, yet progress remains uneven.
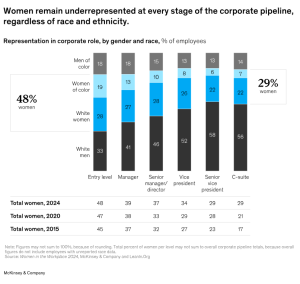
The representation of women declines as one moves up the corporate hierarchy, with only 39% in manager roles and 28% at the senior vice president level. This trend reflects the broader issue of the “broken rung” in the corporate ladder, where women are less likely to be promoted to managerial positions, with just 81 women promoted for every 100 men in 2024. This issue disproportionately affects women of color, who remain severely underrepresented, holding only 7% of C-suite roles.
Despite some positive changes, such as enhanced parental support and increased workplace flexibility, many companies are scaling back programs designed to promote gender and racial diversity. A significant portion of organizations still lacks comprehensive strategies to address bias in hiring and promotion practices, with only about one in four companies implementing critical debiasing practices. Moreover, employees report little improvement in their day-to-day experiences, with many women expressing concerns about insufficient support from managers and ongoing microaggressions.
Looking ahead, the report projects that achieving gender parity will take 22 years for White women and 48 years for women of color in senior leadership roles.
Recommendations
Most organizations need to adopt more effective practices that promote women’s advancement. A best practices checklist, informed by key policies linked to improved outcomes for women, can help organizations identify gaps and explore further opportunities for growth. Based on insights from the report, McKinsey suggests that organizations should focus on four key building blocks:
- Understanding importance: Employees must comprehend why new practices are essential.
- Skill development: Build employees’ skills to implement these practices effectively.
- Supporting mechanisms: Establish systems that reinforce and support new practices.
- Leadership role modeling: Leaders should exemplify the desired behaviors.
While many organizations implement some of these actions, few integrate all four comprehensively. Furthermore, companies can take specific actions to enhance progress in advancing women and fostering inclusion:
- Debiasing processes: Revise hiring and promotion processes to eliminate biases.
- Inspiring allyship: Equip employees with tools to curb biases and engage in allyship.
- Empowering managers: Leverage managers’ influence on career development and team.





























































