Crime report from TT Club and BSI finds over three-quarters of cargo theft takes place at logistics hubs and warehouses, with Free Trade Zone (FTZ) particularly vulnerable locations.
The report ‘Cargo Crime in Gulf Countries and Regional Free Trade Zones’, aims to be a risk mitigation tool for transport operators. Its key highlights regard the following;
- 76% of cargo theft is from warehouse and storage facilities
- Crime hot-spots in UAE & Saudi Arabia
- High-value goods such as electronics targeted
- Insider assistance and corruption plays a prominent role
Smuggling of illicit contraband prevalent in Free trade Zones (FTZ)
The report highlights that warehouse thefts and supply chain corruption are the stand-outs, with a concentration on higher risk areas across the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA).
The role special economic zones play in the Middle East also effects regional disparities in cargo theft.
TT Club’s Mike Yarwood comments:
Regular updates of this nature are essential as criminal gangs are constantly altering their points of attack. The current prevalence of supply chain congestion, delays, disruption, and in the Middle East region in particular packed warehouses, makes such information critical
Furthermore, as Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) economies return to pre-pandemic levels, and data provided by the International Road Transport Union (IRU) is projecting growth in trade, it is possible that criminals will also seek to exploit these higher volumes of cargo throughput to introduce illicit drugs and counterfeited products into shipments.
As well as financial damage these incidents can cause severe operational disruption and unquantifiable reputational damage to supply chain service providers. As a consequence, it remains of key importance to the transport industry to identify, prevent and report any criminal activity
Mr. Yarwood added.
Risk mitigation
Effective management controls to mitigate cargo theft as well as illicit drugs and counterfeit goods being introduced into the legitimate supply chain must combine robust procedural and physical measures on the part of the logistics operator. The following infographic highlights the key issues to consider in mitigation of these areas of risk.
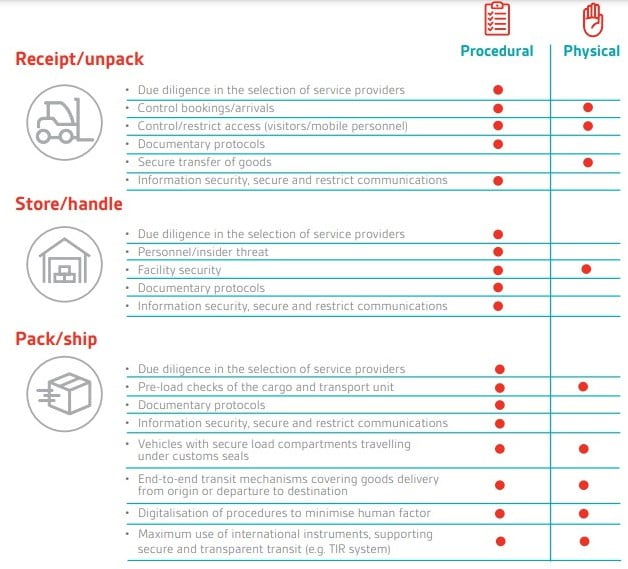
Moreove, regular reviews and audits of both processes and physical measures will serve to ensure that they remain effective, functional and relevant.