In daily life, anger often arises, clouding judgment and straining relationships. Stemming from frustration, disappointment, or injustice, its impact reverberates through our interactions. Anger management involves understanding triggers, controlling intensity, and developing healthier expressions. It’s a way toward emotional balance and healthier relationships.
What is anger?
According to American Psychological Association, anger is a feeling marked by hostility towards someone or something that you perceive has intentionally harmed or offended you.
When handled effectively, anger can provide a constructive means of venting negative feelings and can even fuel problem-solving endeavors. Nonetheless, excessive anger can pose problems. The physiological consequences of intense anger, like elevated blood pressure, may hinder cognitive abilities and have adverse effects on overall physical and mental health.
What is Anger Management?
Anger management does not revolve around completely suppressing anger, as striving to never feel angry is impractical due to its natural emergence despite attempts to contain it. Instead, anger management entails channeling these emotions constructively without succumbing to loss of control. Similar to acquiring any skill, mastering anger management demands dedication, but with practice, it becomes increasingly natural and automatic. Regulating anger and expressing it in a healthy manner can improve relationships, aid in accomplishing objectives, and foster a more satisfying and harmonious life.
Anger management in the workplace
Whether the source of your anger lies in past events or current situations, reflecting on our interpretations and responses can aid in developing better coping mechanisms and anger management skills. In the workplace, individuals often struggle to manage escalating demands on their time and emotions.
What leads to anger in workplace?
- Stress – One of the primary triggers of workplace anger could stem from stress, which may arise from factors such as excessive workloads, inadequate working conditions, unsafe work environments, or challenging interactions with colleagues and clients.Top of Form
- Poor management – Ineffective leadership may involve micromanagement, criticism without constructive feedback, unrealistic or fluctuating expectations, unclear instructions, improper task assignments, abuse of authority, dissatisfaction with procedures, unfair treatment, feeling undervalued, or lacking support.
- External issues – Employees may sometimes bring their personal stressors into the workplace, leading to unexpected anger or aggression triggered by seemingly insignificant events that would not typically provoke such reactions
Tips to manage and control anger
#1 Focus on your breath: Inhale slowly and deeply, then exhale through your mouth. You may find it beneficial to count your breaths as you do this.
#2 Carry a small item that you can hold onto and concentrate on whenever you experience anger. This could be anything like a marble, a fidget toy, or a piece of fabric.
#3 Relax your muscles: Engage in progressive muscle relaxation by deliberately tensing and then gradually relaxing different muscle groups in your body, one by one.
#4 Write your thoughts: Capture your emotions and desired responses on paper. Engaging in this process can aid in calming yourself and reflecting on the circumstances that triggered your emotions.
#5 Get in a quick workout: Anger often generates a surge of energy within you. One effective method for managing anger is to channel this energy through physical exercise.
#6 Take a break: Taking a break from the cause of anger enables you to detach, calm down, and restore emotional equilibrium.
#7 Practice problem-solving: Break complex problems into smaller parts, brainstorm different approaches, and evaluate the possible results of each option.
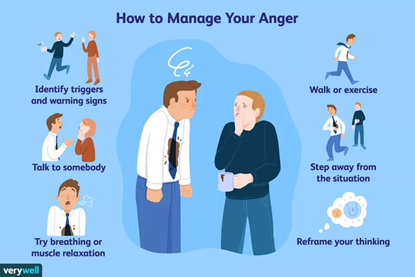
In conclusion, managing anger is crucial for maintaining healthy relationships and overall well-being. By understanding the triggers of anger, practicing relaxation techniques, improving communication skills, and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can effectively cope with and reduce feelings of anger. It’s essential to remember that anger is a normal emotion, but how we choose to respond to it can make a significant difference in our lives and the lives of those around us.



































































