Cyber-attacks are calling the shipping industry to take crucial steps. Several attacks have been reported until now, with the most recent, the attack against the IMO. These incidents outline the importance to invest in cyber security as shipping accelerates its path towards digitalization.
In fact, COVID-19 is calling for more and rapid digital evolution, in order for the industry to survive and opt for more effective operations. Yet, digitalization is a new path for the sector, making it difficult to deal with, on the one hand, while on the other, the sector has shown great signs of maneuvering through smart options and changes.
Steps to handle a potential attack
The first and most important tip is training, which will ensure that all employees, according to their positions, will be able to handle such an incident.
Step 1: Know which are the most usual cyber threats
A recent report conducted by ENISA analyzes which have been the top cyber threats in the timeframe between January 2019 to April 2020.
Accordingly, they gathered the top 15 threats, which are the following:
- Malware
- Web-based Attacks
- Phishing
- Web Application Attacks
- SPAM
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS)
- Identity Theft
- Data Breach
- Insider Threat
- Botnets
- Physical Manipulation, Damage, Theft and Loss
- Information Leakage
- Ransomware
- Cyber Espionage
- Crypto-jacking.
“Knowing your enemy” means that you will be prepared and implement an analysis, as well as a plan if an attack occurs. Moreover, it is important to identify and control who has access to the attacked information and conduct background checks.
Step 2: Move into cyber security action mode
When the attack occurs, keep in mind that it is important to have installed and updated an anti-virus, anti-spyware and other anti-malware program, that will definitely assist you.
In addition, man a team consisting of experts, such as an IT team, data forensics experts, that will help you determine the size and scope of the attack.
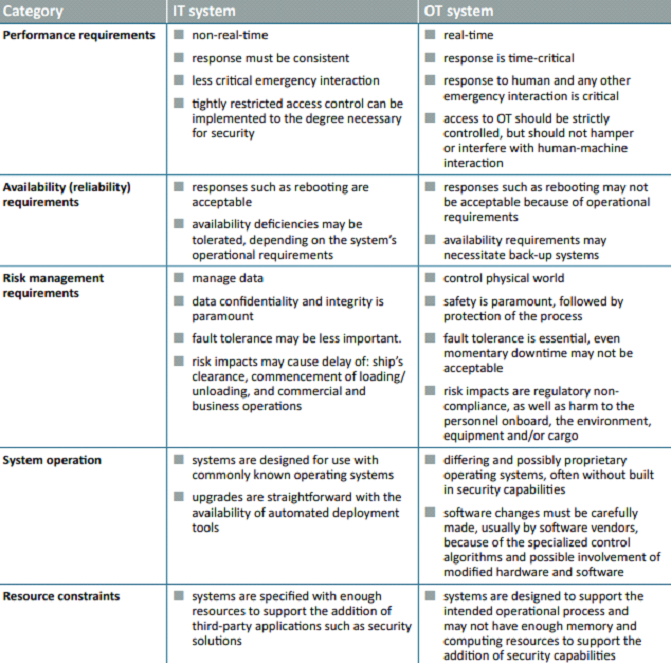
Keep in mind that OT systems control the physical world and IT systems manage data. OT systems differ from traditional IT systems. OT is hardware and software that directly monitors/controls physical devices and processes. IT covers the spectrum of technologies for information processing, including software, hardware and communication technologies. Traditionally OT and IT have been separated, but with the internet, OT and IT are coming closer as historically stand-alone systems are becoming integrated.
Below, ICS has issued a table explaining the differences between OT and IT teams.
Step 3: Assess risk exposure
In a report, the ICS along with additional shipping players, highlight the importance of determining the likelihood of vulnerabilities being exploited by external threats.
They advise to
Determine the likelihood of vulnerabilities being exposed by inappropriate use. Determine the security and safety impact of any individual or combination of vulnerabilities being exploited.
Step 4: Develop protection and detection measures
It is recommended to reduce the likelihood of vulnerabilities being exploited through protection measures, and reduce the potential impact of a vulnerability being exploited.
Tips to detect a cyber-attack are:
- Identify mysterious emails, such as phishing.
- Note unusual.
- Password activity.
- Identify suspicious pop-ups.
- Report a slower-than-normal network.
- Keep software up-to-date.
- Unexpected or sudden changes in available disk space or memory.
Step 5: Establish contingency plans
Develop a prioritized contingency plan to mitigate any potential identified cyber risk.
It is important to understand that cyber incidents may not disappear by themselves.
If for example, the ECDIS has been infected with malware, starting up the back-up ECDIS may cause another cyber incident. It is, therefore, recommended to plan how to carry out the cleaning and restoring of infected systems.
Being informed about any recent cyber incidents, the kind and the impact they had, could be used to improve the response plans of all ships in the company’s fleet and an information strategy for such incidents may be considered.
Step 6: Recovery
After a cybersecurity breach, you’ll need mechanisms in place to help resume normal operations.
Find how the attack occurred and whether there was a breach in your security systems or it was the outcome of a human error and then move towards improving the existent processes, procedures and technologies.
Keep in mind that it is crucial to make full backups of important business data and information, while also continue to schezule incremental backups.