Ponemon Institute presents the results of the second annual study on the 2017 State of Cybersecurity in Small and MediumSized Businesses sponsored by Keeper Security. The goal of the study is to reveal how smaller companies are addressing the same threats larger companies face. Approximately 600 individuals in companies with a headcount from less than 100 to 1,000 participated in this research.
Generally, cyber attacks, ransomware and disruptive technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), challenge the ability of small businesses to safeguard their information assets. In fact, only 21 % of the companies represented in this study rate their ability to mitigate cyber risks, vulnerabilities and attacks as highly effective.
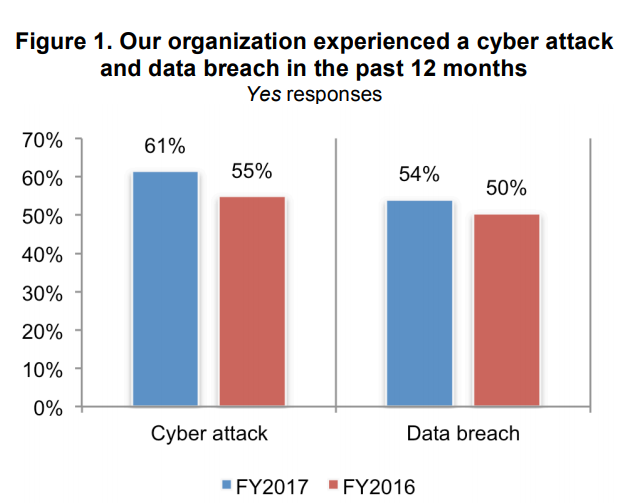
According to the research, the top trends in the state of cybersecurity in SMBs are:
- Cyber attacks affected more SMBs in the past year, an increase from 55 % to 61 % of respondents. This year’s research resulted to the fact that cyber attacks are better-targeted and more sophisticated.
- The rise of ransomware is affecting SMBs. Specifically, 52 % of respondents say their companies experienced a ransomware attack and 53 % of these respondents say they had more than two ransomware incidents in the past 12 months.
- SMBs are having slightly more data breaches involving personal information and the size of data breaches is larger. From the participants, 54% support that the root of the attack were negligent employees.
- Internet of Things (IoT), seems to be concerning the 67 % of respondents, saying that their organizations are very concerned or concerned about the security of IoT devices in the
workplace. - Exploits and malware have evaded their intrusion detection system, and anti-virus solutions.
- Passwords are targeted and 59 % of respondents say they do not have visibility into employees’ password practices such as the use of unique or strong passwords and sharing passwords with others.
- Password policies are still not strictly enforced.
- Personnel, budget and technologies continue to be insufficient to have a strong security posture.
- Cyber attacks are more costly. The average cost due to damage or theft of IT assets and infrastructure increased from $879,582 to $1,027,053.
Moreover the types of cyber attacks, according to the research, are: 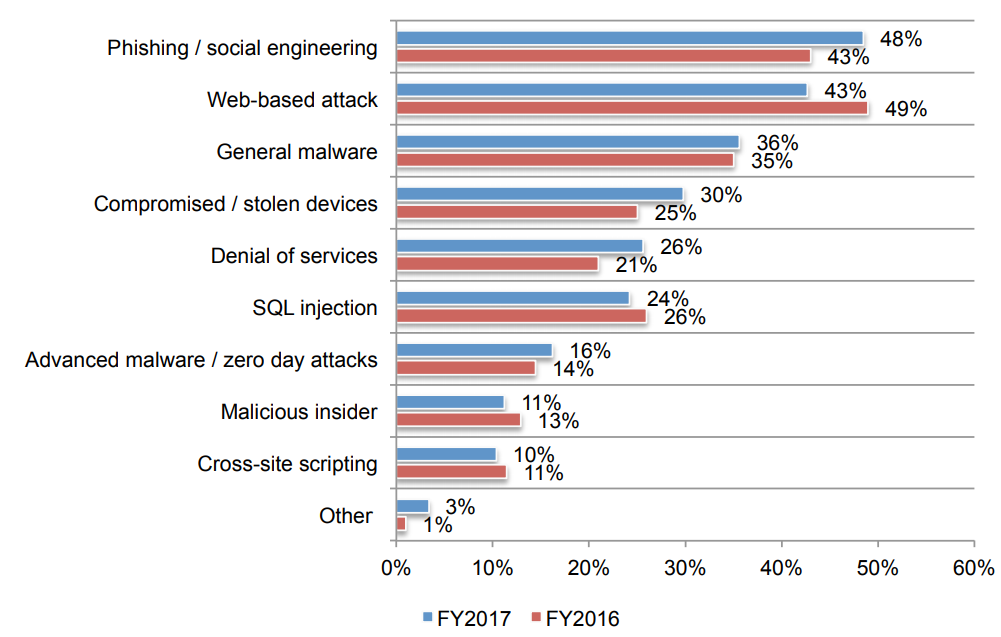
- Phishing / social engineering;
- Cross-site scripting;
- Malicious insider;
- Advanced malware / zero day attacks;
- SQL injection;
- Denial of services;
- Compromised / stolen devices;
- General malware;
- Web-based attack;
- Other.
Concluding, the routes of cyber attacks, most commonly, are:
- Malicious insider;
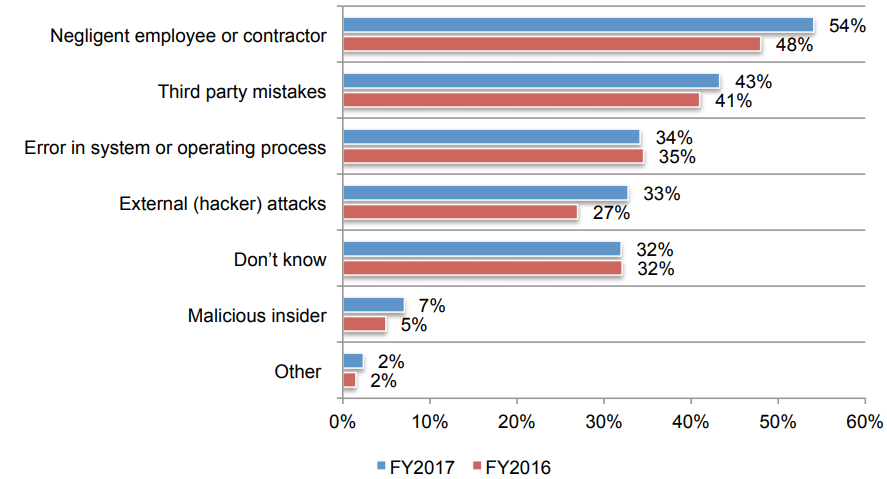
- External (hacker) attacks;
- Error in system or operating process;
- Third party mistakes;
- Negligent employee or contractor;
- Other.