NYPA (New York Power Authority) published its completed study on European offshore wind transmission models that will help New York head towards its 9GW by 2035 goal. The study focused on transmission and interconnection strategies, while also development and electricity rate structures in the United Kingdom, Germany, the Netherlands and Denmark, which enabled each country to lower its costs over time.
The study reports that the researchers found many successful approaches and ways on developing an offshore wind system.
Accordingly, key conclusions that arose from the study are:
- Planning for scale and encouraging healthy competition have been key to the growth of offshore wind in the four countries studied (Denmark, the Netherlands, Germany and the United Kingdom).
- Transparent, long-term, on and offshore grid planning removes barriers to entry, improves coordination and lowers costs.
- In Europe, cross-border coordination has helped countries leverage planned transmission infrastructure, provide resource flexibility and take advantage of economies of scale.
- Long-term grid planning for both on and offshore, coordination and performance incentive alignment are really important so parties are incentivized to finish projects in a timely manner.
LIPA CEO Thomas Falcone commented
As New York gears up for the rapid development of offshore wind under Governor Cuomo’s leadership, having a better understanding of Europe’s already-thriving industry will provide key insights as we look to build a skilled workforce and develop our ports.
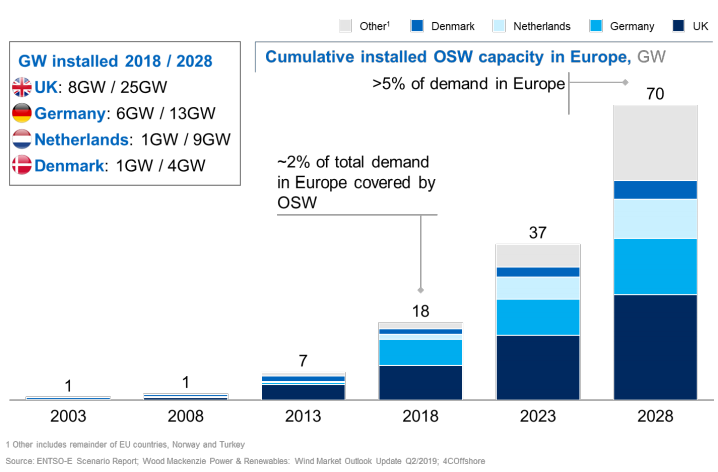
OSW installed capacity in Europe is expected to increase four-fold over ten years from ~18GW installed in 2018 to ~70GW in 2028. The study focused on the four countries above, the United Kingdom, Germany, the Netherlands, and Denmark.
These four countries have different geographic characteristics:
- From the small (Denmark: 6M people, 6GW peak load) to the populous (Germany: 83M people, 80GW peak load)’
- Coastlines from the constrained (Netherlands: 280 miles) to the expansive (UK: 7,700 miles).
NYPA led the study, while other project partners include New York Independent System Operator (NYISO), Con Edison, New York State Energy Research and Development Authority (NYSERDA), Long Island Power Authority (LIPA) and the National Grid.
To explore more click on the PDF herebelow
































































