As reported earlier in 2020, South Korea has introduced domestically new environmental laws, applying voluntary speed limits for ships and SOx emission control areas in specific ports, starting from 1st September 2020. Failure to comply with the non-voluntary requirements could result in fines of up to 10 million won or imprisonment, Lloyd’s Register informed.
New Korean SECAs
Effective from 1 September 2020, the following ports become Korean SECAs:
- Incheon (including Gyeongin port)
- Pyeongtaek·Dangjin
- Yeosu·Gwangyang (including Hadong port)
- Busan
- Ulsan
New sulphur fuel limits
Also from 1st September 2020, all ships (including foreign-flagged vessels) berthed or at anchorage in the above SECAs must ensure that…
- 1 hour after completion of berthing until 1 hour before de-berthing; or
- 1 hour after completion of anchoring until 1 hour before leaving anchor,
…sulphur content of fuel oils used onboard does not exceed 0.1% m/m (or an approved equivalent arrangement is used).
Meanwhile, effective from 1st January 2022, all ships (including foreign-flagged vessels) entering or leaving the SECAs must comply with the same 0.1% m/m sulphur fuel limit using the appropriate fuel oils (or approved equivalent arrangement).
Approved equivalent arrangement
The use of an exhaust gas cleaning system (EGCS) will be allowed as an equivalent arrangement if the EGCS is at least as effective in terms of SOx emission reductions (4.3 SO2(ppm)/CO2 (%, v/v)) as compared to using a fuel oil with sulphur content not exceeding 0.1% m/m and satisfies the criteria set by South Korea.
Recording requirements
In addition, ships operating inside Korean SECAs shall record the fuel oil change-over, etc. in the engineer’s logbook, or alternatively record the operation status of the EGCS.
Ships using fuel oils with sulphur content not exceeding 0.1% m/m to comply with the requirements, and changing fuel oils for Korean SECAs shall record:
- Kind of fuel oil and the date, time and position of the ship when fuel-oil-change-over operation is completed;
- The remaining volume of fuel oil in each tank (only applicable to fuel oil with sulphur content not exceeding 0.1% m/m); and
- Sulphur content of fuel oil.
The ship shall keep the above engineer’s logbook on board for a period of not less than 12 months from the time of delivery of the fuel oils to the ship.
Fuel changeover procedure
Ships using separate fuel oils stored in separate tanks (to comply with sulphur content limit requirements) shall carry a written procedure showing how the fuel oil change-over is to be done before entering or leaving a Korean SECA.
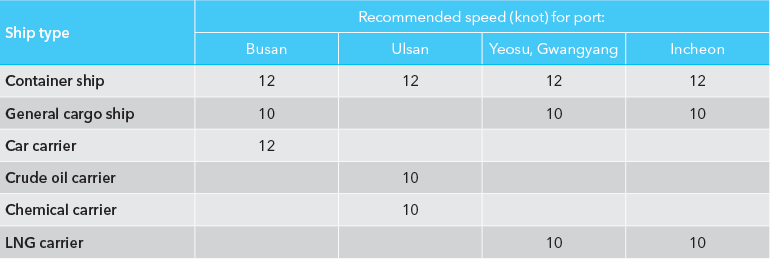
Voluntary Speed Reduction Program
The scheme applies to 5 ports:
- Busan Port,
- Ulsan Port,
- Yeosu Port,
- Gwangyang Port and
- Incheon Port).
Participating ships will receive discounts on port entry/leave fees for complying with the slow-steaming requirements.
Ships covered under for the VSR programme differ at each port, but must be over 3,000GT and among the top 3 “fine-dustemitting” ship-types, according to data by DNV GL.